As we enter 2024, the momentum for the energy transition intensifies. The four forces of change (political, investor, consumer and microeconomic) are placing significant pressure on organizations. They highlight a stark reality for businesses that inaction is no longer sustainable. Our e-book, based on the views from Enverus Intelligence® Research (EIR), is a carefully curated compilation of the pivotal research findings from our energy transition team. Learn from this wealth of knowledge so you can make a profound difference in your strategic business decisions.
Disclosure: Enverus Intelligence Research, Inc., a subsidiary of Enverus, provides the Enverus Intelligence® | Research (EIR) products. See additional disclosures.

Explore the wider “realm of coverage” in energy, from decarbonization and subsurface innovation to power asset advancements. The ETR Team will dissect energy transition themes for 2024, pinpointing where business strategies meet viable funding and highlighting the technologies set to commercialize and drive new capital. Learn how heightened shareholder expectations interplay with the current inflation and interest rate scenario to create investment opportunities. Moreover, understand how the emissions gauntlet and how execution is becoming the new battleground with the shift from regulatory compliance to operational efficiency.
Date Published: (01/11/2024)
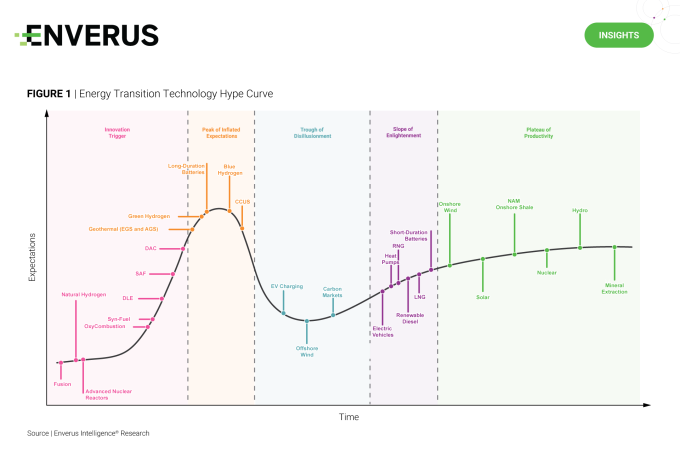
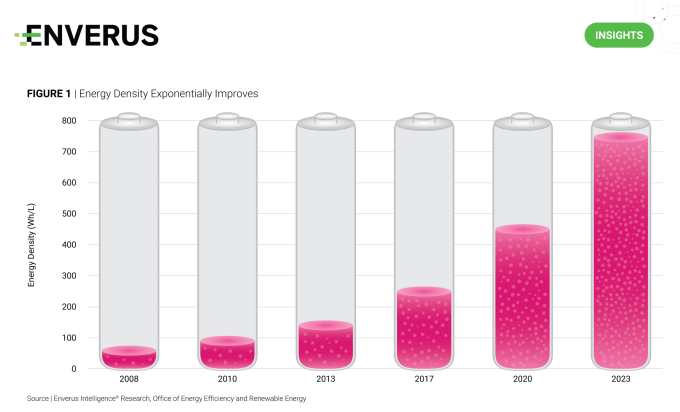
EIR plots new and emerging technologies along a hype curve to illustrate the life cycle of these technologies from ideation to full-scale commercialization. In its most recent update (Figure 1), a few key additions and movements are important to note.
Direct air capture (DAC) has grown substantially with significant government support. Improvements in capture sorbents and solvents that reduce energy and water requirements are needed to bring down costs for the momentum to continue.
Blue hydrogen project announcements will outpace green in the near term, reflecting limited electrolyzer manufacturing capacity, increasing costs and stringent rumored 45V PTC requirements. Blue hydrogen benefits from strong CCUS incentives, low gas prices and progress in carbon sequestration projects.
Direct lithium extraction (DLE) has moved up the hype curve. Numerous pilots have started, and early phase construction has begun on Standard Lithium’s (SLI) phase 1 commercial project. EIR expects this momentum to continue with interest from supermajors, such as project commitments by XOM and interest from CVX and OXY. A key risk is sub-$10,000/tonne lithium carbonate equivalent spot prices.
Sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) adoption will be ahead of market expectations with global production at least doubling in 2024 due to increased demand from national and regional airlines, spurring several greenfield projects in the U.S. to reach FID.
Date Published: (12/28/2023)
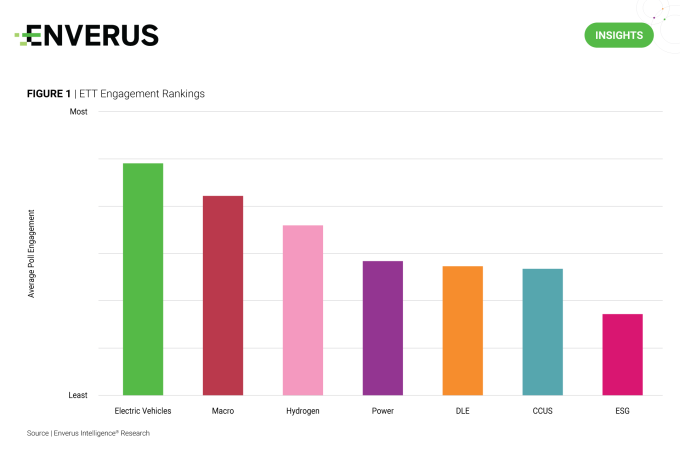
To mark the first year of Energy Transition Today, EIR is reviewing statistics from poll questions on power, CCUS, hydrogen, ESG and other issues. The most engaging topics for readers focused on electric vehicles and macro/policy discussions: How likely are you to purchase an EV as your next vehicle? More than 100 readers responded, with 47% clicking the hard no button and 53% selecting either the very likely or undecided options.
Power
Swapping out coal for carbon-neutral power sources was a clear winner in strategy to reach global warming targets, but some alternative technologies like hydrogen and nuclear were on the naughty list, according to poll results. The latter came despite 100% voting that a nuclear renaissance was essential for California to hit 2045 clean energy targets. At the national level, you voted that the most likely reason to fail to hit GHG emission reduction targets by 2030 was an underinvestment in renewable energy sources. Regardless of your stance on the “energy transition,” everyone agreed new technologies are required to deviate from today’s status quo.
Subsurface
It was a big year for subsurface innovation with headline-worthy investments in CCUS and DLE from some of the biggest players (OXY and XOM) in the North American oil and gas space. Acquisitions of Denbury and Carbon Engineering as well as investments in an array of DLE projects bring a lot of optimism for 2024 subsurface activity. EIR is on the same page that oil and gas wastewater could play a surprising role in lithium production, and that standalone brine-producing wells could be a norm in the mining space. Regulatory hurdles and cost constraints were EIR’s key concerns for CCUS; now that dozens of applications have been submitted, EIR will see if pipeline woes continue to be a constraint for project feasibility.
Low carbon fuels
Hydrogen was a hot topic. Concerns around energy efficiency and policy support didn’t stop the DOE from selecting seven hubs around the country for project construction. EIR believes hydrogen needs an extension on 45V production credits to ensure long-term health for the industry. Poll results indicated a cautious optimism toward the new technology. ESG isn’t receiving a tonne of love from investors or attention from readers, as those polls averaged the lowest engagement.
Reflecting on EIR’s journey so far, it is evident the pursuit of a sustainable energy future involves navigating diverse perspectives, technological challenges and regulatory considerations. The shared commitment to exploring new solutions highlights the importance of collaborative efforts in addressing the complex global energy landscape. EIR looks forward to continuing to help separate the winners from the losers in 2024.
Date Published: (02/01/2024)
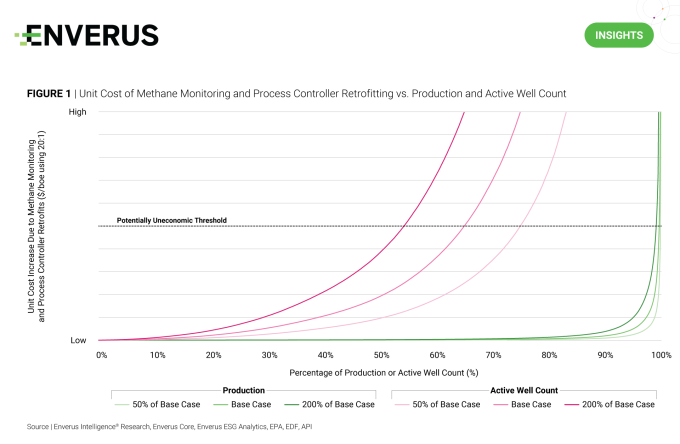
EIR’s analyst teams have gone through the EPA’s recently approved Quad O regulations and concluded this will represent a step change in fixed costs that will accelerate P&A timelines. Investors and operators should really begin modeling these implications now and EIR’s new report will be useful in understanding how these new regulations will impact the industry.
The EPA released the ~1,700-page final rule for New Source Performance Standards OOOOb and Emission Guidelines OOOOc (collectively known as Quad O) in December after more than two years in the making. The EPA’s intention for Quad O is to reduce “super pollutant” methane emissions from the oil and gas industry by ~80% by 2030 through updated performance standards. Required procedures will be applied to new or recently modified facilities through OOOOb and to existing facilities through OOOOc.
Quad O will have a direct and material impact on the U.S. oil and gas industry. It targets many different sources of methane by: 1) mandating extensive operator-run leak detection and repair (LDAR); 2) requiring the retrofitting of process controllers (previously referred to as pneumatic controllers), flare stacks and pneumatic pumps; 3) placing restrictive limits on associated gas flaring; and 4) implementing an EPA-run super-emitter response program that will rely on certified third parties to detect and notify the EPA of large, irregular emission events surpassing 100 kg/hr of CH4.
EIR’s cost impact analysis revealed that 34% of active wells, or 285,000, could see an added $10/boe in methane monitoring and process controller retrofitting costs, a threshold EIR believes could make these wells uneconomic (Figure 1). While country-level production will remain largely unaffected, extremely marginal wells with little to no revenue to absorb the higher fixed costs will be the most impacted by the regulations in the next five years.
EIR sees this trend forcing hundreds of thousands of wells into earlier-than-planned retirement as operators grapple with the costs of bringing sites into compliance or accelerating P&A programs. This will have a ripple effect on OFS companies, loan-providing banks, state regulators with orphan well programs and local economies that rely on the continuing operations of these companies.
Date Published: (12/21/2023)
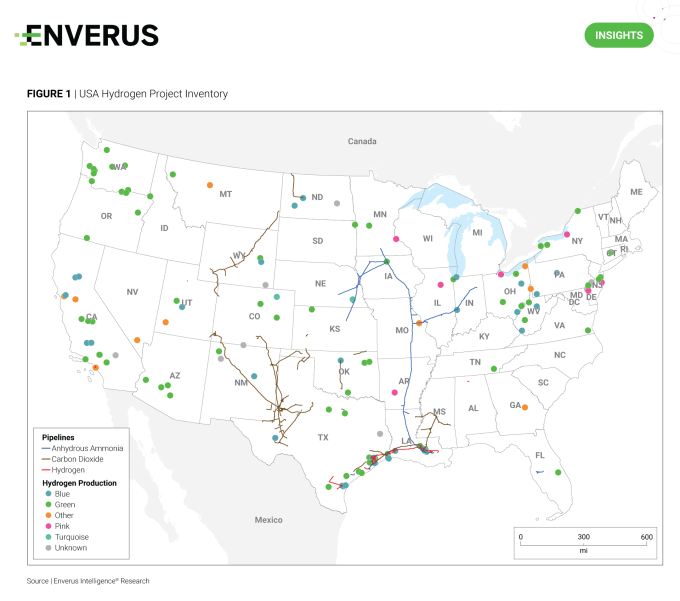
The U.S. clean hydrogen sector has undergone rapid expansion following the IRA and DOE hub funding announcements. According to EIR’s Hydrogen Project Tracker, 180 projects could be operational by 2030, which is a seven-fold increase from the current count. Project locations typically align with underlying resource quality, where green production mirrors low-cost renewable generation in areas like central and southwest U.S, while blue projects favor low-cost gas and saline sequestration basins like the Gulf Coast. The DOE is also encouraging geographic diversity with hubs spread across the country, resulting in funding recipients outside of top-tier regions, such as the Pacific Northwest or Atlantic Northeast (Figure 1).
EIR notes that only 8% of clean hydrogen projects planning to commence operations by 2030 have secured a final investment decision. This lagging figure is predominantly driven by operators’ inability to secure long-term offtake contracts and uncertainty surrounding the 45V PTC tax credit guidelines. Many companies are considering exports to European and Asian markets, but they must first evaluate the emissions intensity of production to ensure incentive eligibility both stateside and overseas.
Date Published: (11/23/2023)

The DOE recently announced seven clean hydrogen hubs eligible for a combined $7 billion in public funding (Figure 1). Each hub developed a unique hydrogen production strategy that was chosen to best utilize the regionally available resources such as renewable energy type and quality, nuclear availability, existing infrastructure and carbon sequestration basin viability.
Across these metrics, the Gulf Coast’s HyVelocity hub stands out above the rest with excellent renewable energy resources in western Texas, extensive CO2 and H2 pipeline and storage infrastructure, and world-class carbon sequestration basins. Furthermore, the Gulf Coast is home to the highest concentration of primary hydrogen use cases which include refining, ammonia, petrochemical and steel production, and power generation. EIR estimates the HyVelocity hub is surrounded by the largest number of these brownfield facilities within a 30-mile radius (70), followed by the Mid-Atlantic Clean Hydrogen Hub (49) and the Midwest Alliance for Clean Hydrogen hub (46).
Date Published: (11/02/2023)
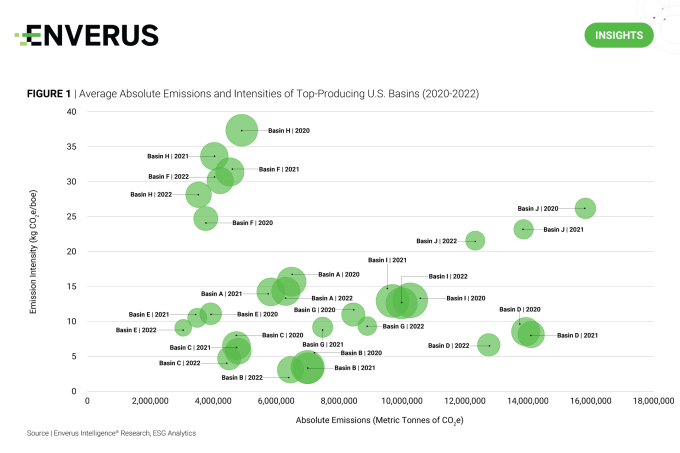
Emission intensities in the U.S. upstream sector dropped by 15% since 2020, based on the latest 2022 EPA FLIGHT data released in early October. Absolute annual emissions fell from 97.2 to 88.5 million metric tonnes (Mt) CO2e over the same period, mainly driven by decreases in venting and flaring emissions.
EIR attributes the 8.9 Mt CO2e decrease in venting emissions to widespread retrofitting of intermittent bleed pneumatic controllers and increased surveying of equipment for leaks, rather than utilizing population counts and emission factors. Consequently, reported methane emissions fell across nine of the top 10 largest basins by production, except for Fort Worth.
However, even after the decreases, six of the top-producing basins would have on average breached the proposed 0.20% upstream intensity threshold for the IRA’s methane fee: the DJ, Western Gulf, Anadarko, Williston, Fort Worth and San Juan. EIR expects continued progress toward methane reduction targets will help to minimize the fee’s impact on operators from 2024 onward.
Date Published: (01/18/2024)
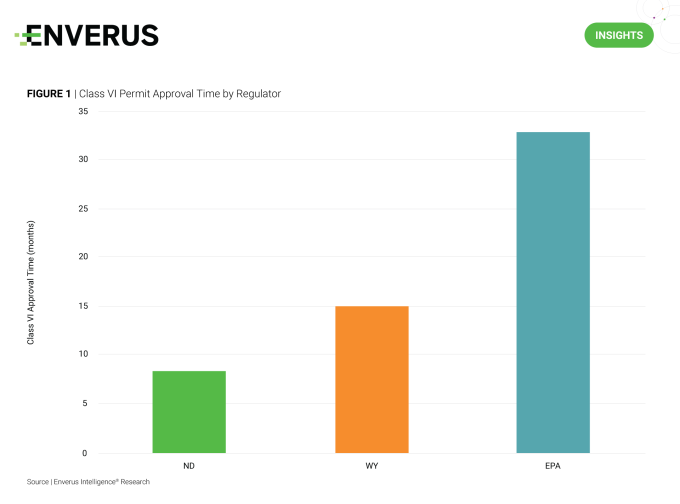
Louisiana’s Class VI primacy approval at the end of 2023 is a big step forward for CCUS project development. This change will help alleviate the backlog of applications awaiting approval from the EPA, as 35% (22 of 63) of projects currently under review with the federal agency are in Louisiana. States in EPA Region 6 stand to benefit the most from the exiting Louisiana projects, with only 11 remaining in that region: eight in Texas and one each in New Mexico, Oklahoma and Arkansas.
Louisiana should also benefit from the change, as Class VI permit approval timelines have been significantly shorter in states with primacy. The other two states with primary enforcement authority, North Dakota and Wyoming, have just three and one projects currently in review, respectively, compared to the 22 projects just received by Louisiana. North Dakota’s two issued Class VI permits (Blue Flint and Red Trail) took only eight months and nine months to receive permit approval, and Wyoming’s recent approval (Sweetwater) took 15 months. These timelines are well below what EIR is seeing for the EPA approval process. For example, the Wabash Carbon Services project in Indiana expected to receive permit approval within the next month has been under review with the EPA for 33 months.
As the current Class VI applications in Louisiana get transferred to its Department of Natural Resources Feb. 5, EIR will see if the state’s primacy helps speed up the review phase and when Louisiana gets its first Class VI well.
Date Published: (11/30/2023)
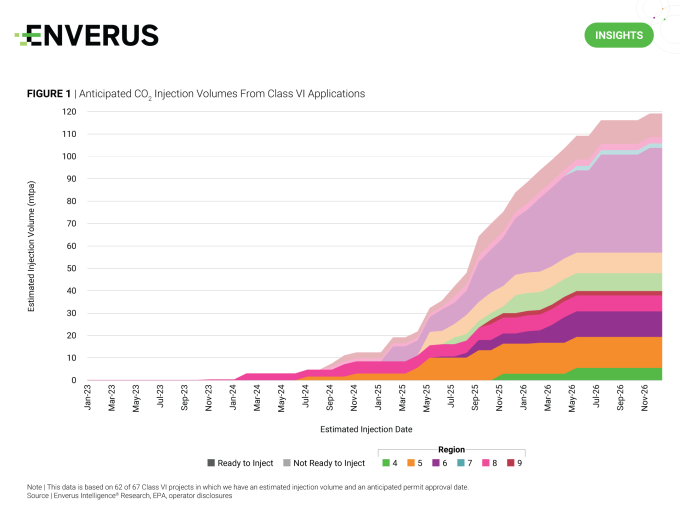
Numerous takeaways can be drawn regarding the status of and opportunities for CCUS by extracting information from the Class VI permitting process. Looking at current and expected rates of CO2 injection through time, EIR can draw essential insights into the source-to-sink value chain to help screen for future partnerships, investments and market demands for midstream and OFS operations.
Anticipating the EPA’s timeline for Class VI permit approvals and considering the Class VI applications from North Dakota and Wyoming, the two states with primacy, it is conceivable that final approvals may be granted to 167 applications spanning 61 projects by 2026. This would result in the creation of capacity enabling the injection of nearly 120 mtpa, as illustrated in Figure 1. The majority of this injection capacity hinges on factors such as infrastructure development, facility construction and sources of CO2 that are yet to be determined.
To leverage the likelihood of all those factors aligning to commence injection upon approval, Enverus assigned “ready” and “not ready” to inject labels to the permits currently in the queue. The result of this analysis suggests EIR can expect 40 mtpa of approved, permitted capacity to engage in active injection shortly after permit approval, amounting to just more than 30% of available injection capacity, by mid-2026.
Date Published: (11/09/2023)
Enverus Energy Transition Research’s CCUS team has rebranded as the Subsurface Innovation team covering CCUS, DLE, geothermal, natural hydrogen and helium. Amid a rapidly evolving sector, this team has tracked 114 project announcements, partnerships and mergers (Figure 1).
CCUS
DLE
Geothermal
Helium
Natural hydrogen
Date Published: (01/25/2024)
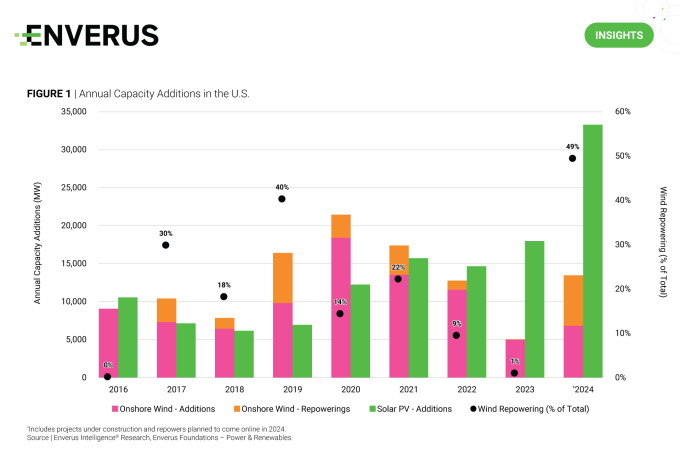
Solar capacity additions now surpass onshore wind additions by a significant margin, as illustrated in Figure 1. While both technologies grapple with inflation and supply chain challenges, solar has experienced a more rapid improvement in cost and efficiency. Nevertheless, revitalizing older wind projects through repowering, involving the retrofitting of existing sites with new or refurbished equipment, holds the potential for a renewed period of growth.
In comparison to constructing new facilities, repowering offers shorter permitting times and lower costs by leveraging existing sites and infrastructure. Furthermore, it enhances power production and reduces maintenance expenses by transitioning to higher-efficiency turbines. A repower project can qualify for an additional 10 years of production tax credits, provided that the fair market value of any used property does not exceed 20% of the total value.
As states work to achieve their renewable energy goals, the economic feasibility of revitalizing onshore wind assets will play a vital role in advancing the energy transition.
Date Published: (01/04/2024)
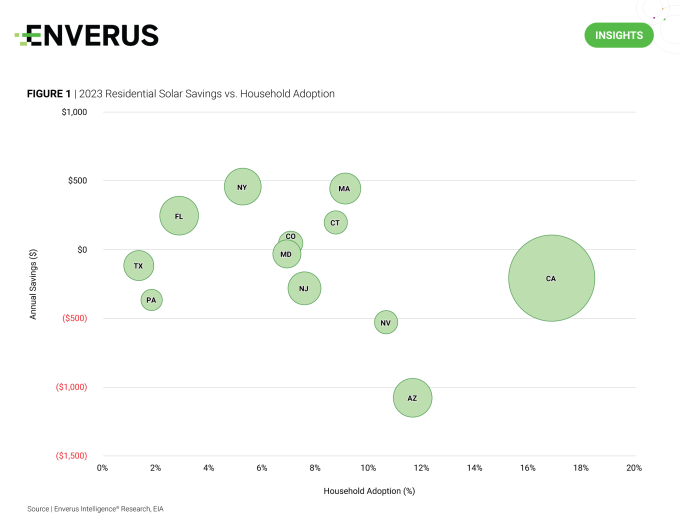
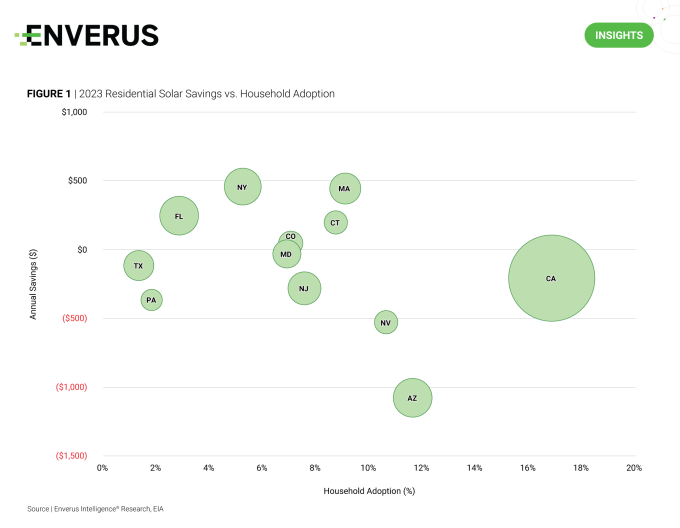
The residential solar industry faced significant disruption in 2023, driven by a high interest rate environment that resulted in a ~40% trailing 12-month decrease in the share prices for some of the largest third-party owners. Anticipating a rise in retail power costs and a decline in interest rates, states that offer appealing residential solar economics are positioned for substantial growth in 2024.
Figure 1 displays the percentage of household adoption in several major states along with the anticipated annual savings if residents were to install new systems in 2023. Maintaining a similar annual savings figure, EIR thinks states like New York and Massachusetts are positioned for notable growth this year, thanks to untapped markets offering economic opportunities.
Date Published: (12/14/2023)
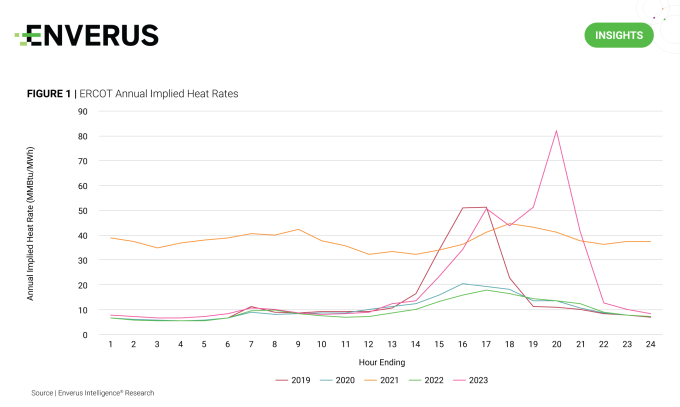
Implied heat rates serve as a useful screen for reliability events and market inefficiencies. Annual implied heat rate is represented as energy prices ($/MWh) divided by natural gas prices ($/MMBtu) averaged by hour of the day. Implied heat rate is also known as the breakeven natural gas market heat rate since only gas-fired plants that have a lower operating heat rate can break even.
Within the system operated by the Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT), extreme weather impacts contribute to higher implied heat rates that exceed typical operating heat rates for gas-fired plants. While the higher implied heat rates in 2021 are easily explained by Winter Storm Uri’s impact in February, 2019 and 2023 deserve a closer look.
High implied heat rate hours in those years coincide with extreme heat in the summer, structural market changes, low natural gas prices and differing levels of congestion. ERCOT’s shortage pricing mechanism was modified in March of 2019 to loosen operating reserve demand curve rules, resulting in more frequent triggering of shortage pricing. This caused an escalation in shortage pricing with August and September contributing to a 32% increase in the 2019 average real-time price.
Throughout the second half of 2023, high implied heat rates were a direct result of the June rollout of the ERCOT Contingency Reserve Service (ECRS). The ECRS program adds approximately 2,500 MW to the total online reserve stack within ERCOT’s ancillary service market. The main purpose for introducing this product was to mitigate the net load variability issues seen alongside high penetration of intermittent generation. Despite best intentions, the ECRS rollout caused unforeseen consequences by effectively paying thermal plants to enter the ECRS market while staying out of the energy market. This resulted in higher energy market prices as the marginal unit was pushed further up the offer curve.
Date Published: (12/07/2023)
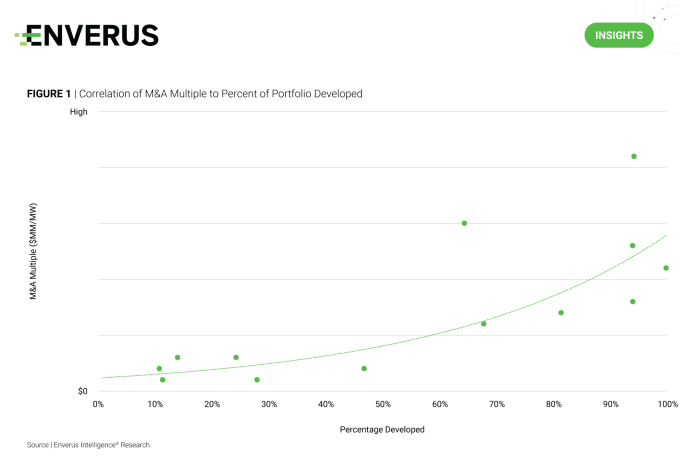
Due to the congestion and high rates of failure in the interconnection queues, EIR expects only a fraction of planned generation projects to come online. This is a critical factor to keep in mind when screening for acquisition targets in the power generation space.
Looking at recent power generation M&A activity, a higher proportion of operational capacity, relative to total capacity, is consistently associated with a higher valuation multiple (Figure 1). This trend line reflects the price that acquirers are willing to pay for the risk associated with development pipelines that will not fully materialize.
EIR has built a gradient-boosting machine learning model to predict the probability that a project will reach completion or be withdrawn from the queue. This tool allows clients to identify high probability development portfolios that can be acquired at a discount, which would be difficult to do without EIR’s proprietary model.
Date Published: (11/16/2023)
Due to the congestion and high rates of failure in the interconnection queues, EIR expects only a fraction of planned generation projects to come online. This is a critical factor to keep in mind when screening for acquisition targets in the power generation space.
Looking at recent power generation M&A activity, a higher proportion of operational capacity, relative to total capacity, is consistently associated with a higher valuation multiple (Figure 1). This trend line reflects the price that acquirers are willing to pay for the risk associated with development pipelines that will not fully materialize.
EIR has built a gradient-boosting machine learning model to predict the probability that a project will reach completion or be withdrawn from the queue. This tool allows clients to identify high probability development portfolios that can be acquired at a discount, which would be difficult to do without EIR’s proprietary model.
Confidently navigate the volatile energy market, from maximizing the subsurface to reducing emissions in the sky.
Read More about Energy Transition Research
Bring improved accuracy to your power forecasts with AI and machine learning-based load, renewables and price forecasts.
Read More About Power and Renewables
Designed to be informative yet accessible, each 30-minute episode brings industry influencers right to your screen. Together, we delve into diverse CCUS-specific subjects.
.
Read More About CCUS Fireside Chat Webinar Series
oin our host Andrew Gillick for an exciting discussion on the dynamic landscape of the Hydrogen Economy with Dr. Naomi L. Boness, Co-Managing Director of the Stanford Hydrogen Initiative.
Read More About Webinar: The Reality of a Hydrogen Economy
Your guide to navigating the North American and international energy landscape in 2024. Explore commodity prices, well costs, M&A’s impacts and the energy transition challenges and opportunities.
Understand how upstream oil and gas business models best fit with emerging energy transition opportunities and gain context on the best avenues for energy transition participation for an upstream oil and gas operator.
Read More About Energy Transition Opportunities for Operators
Discover
About Enverus
Resources
Follow Us
© Copyright 2024 All data and information are provided “as is”.