
Investors looking to participate in the various ISO administered annual and monthly FTR auctions must navigate a complex landscape of shifting policy and grid topology. Of note for ERCOT market participants is the recent Texas PUC approval of a performance credit mechanism, a major market reform over continued reliability concerns that will go before the state’s legislature this spring.
Adding even more complexity to most U.S. markets in 2023 is the unstoppable force of renewable energy and related infrastructure. This includes a 10% increase in the investment tax credit (ITC) for wind and solar projects built within specific energy communities and up to a 20% ITC increase for Environmental Justice Areas, as defined in the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA).
Whether trading, hedging, or a blend of both, market participants must shape their view of how systems and topology are changing with a complex array of data and analytical tools. To confidently bid and succeed in FTR auctions requires a rigorous methodology to track market events like outages to accurately inform FTR positions, trades and risk strategies.
In this e-book, we will summarize some of the important factors FTR traders will need to review as they prepare for the FTR auctions and the considerations that need to be made:

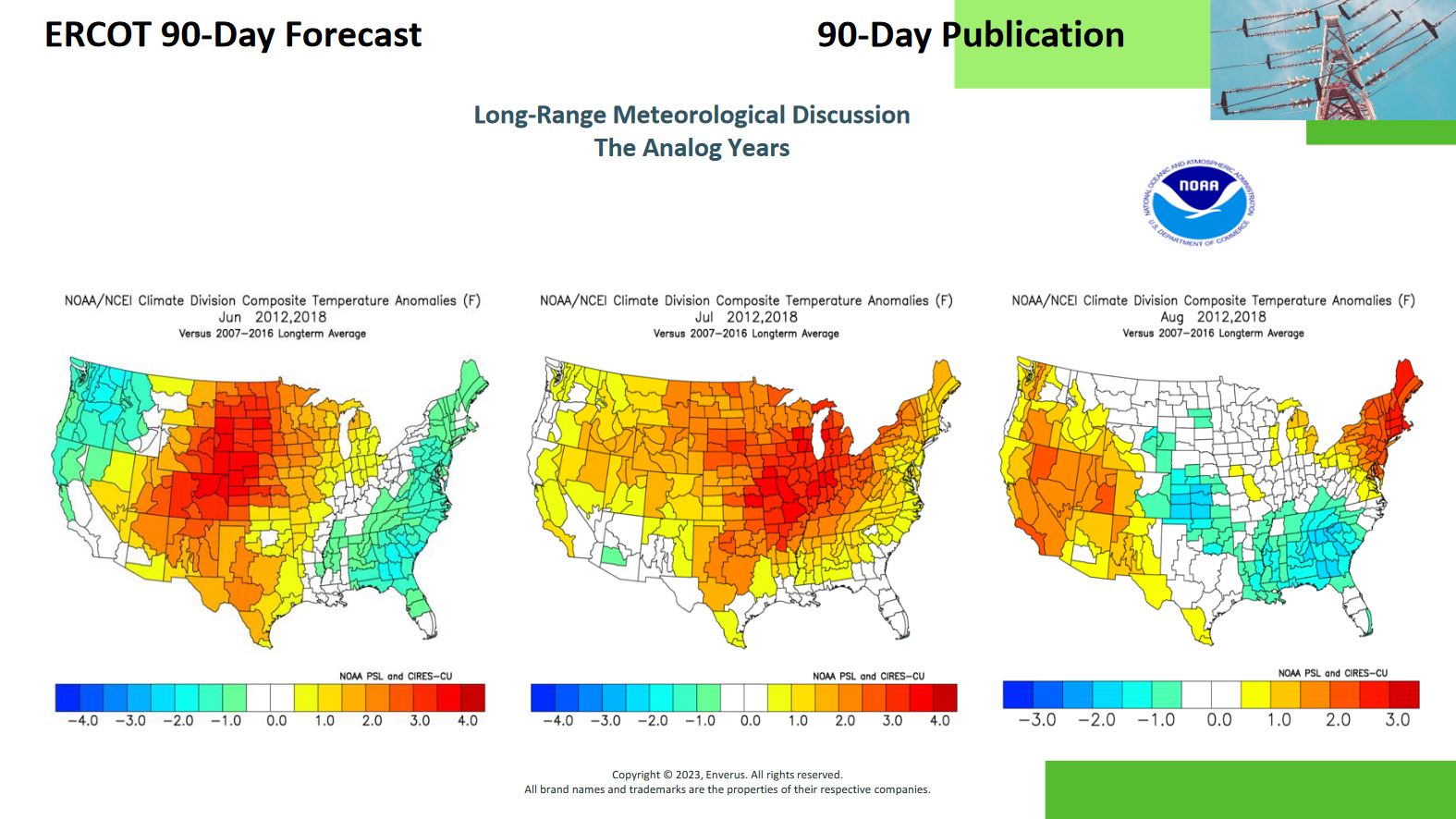
One starting point to study the weather and its impact on the grid is by examining analog years that had similar weather patterns and observing what occurred. If you identify a year where similar weather conditions occur, you can examine what the grid looked like and which paths bound. This analysis can help you narrow down your areas for interesting paths. Note, grid infrastructure changes constantly, so if the analog years you are comparing to is more than a couple years back and there has been significant changes to the power infrastructure since then, the historical view of the grid is a less reliable indicator of what the grid understand similar weather conditions.
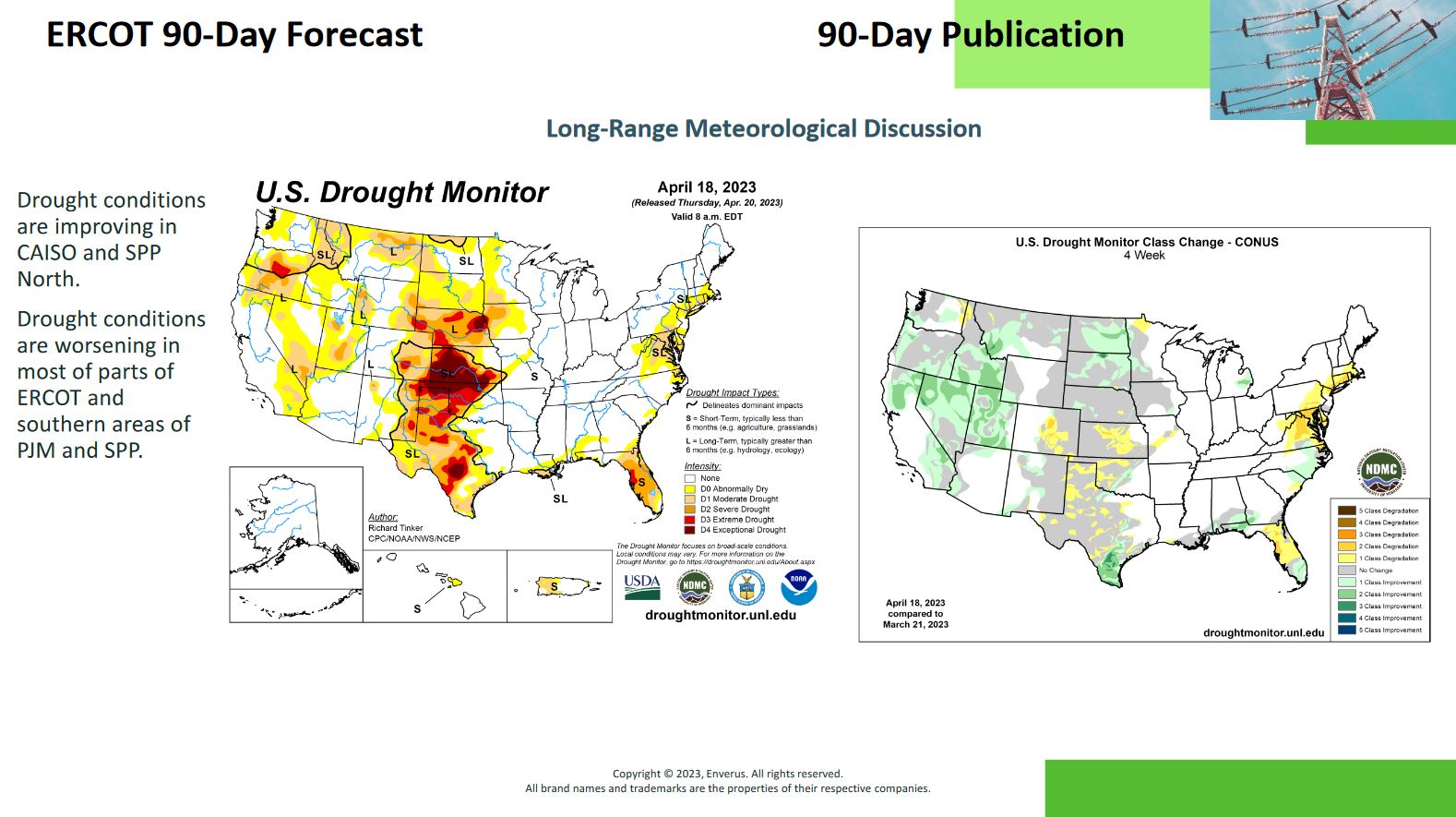
Monitoring drought conditions is also an important weather factor that can impact both load and power generation. When droughts occur, temperatures rise, causing higher load demand as water plays a critical role in keeping surrounding areas cool. Hydro power generation and thermal plants rely on water to generate power, so droughts will have a negative impact on how much power these power plants can generate.
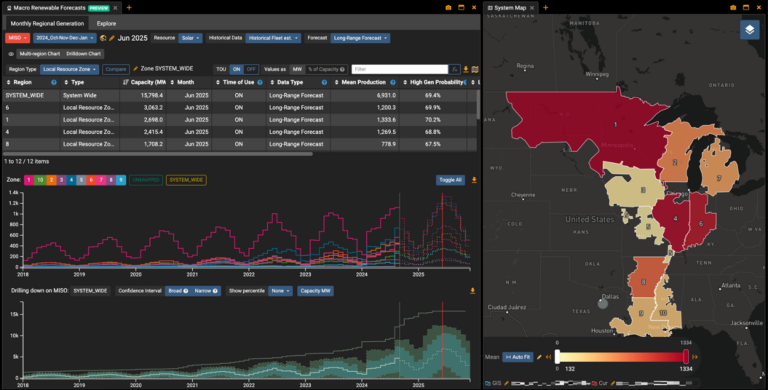
Advanced forecasting solutions can furnish FTR traders with insights into how anticipated temperature fluctuations will impact the grid from the ISO to the nodal level. Through the analysis of historical data and the application of machine learning algorithms, FTR traders can evaluate risk and adapt their strategies accordingly. These solutions can provide both macro and granular forecasts extending months into the future, empowering traders to pinpoint emerging opportunities and refine their trading approaches. Amidst market volatility, these types of forecasts can empower FTR traders to confidently navigate weather-related fluctuations, unlocking new avenues for success in the energy market.
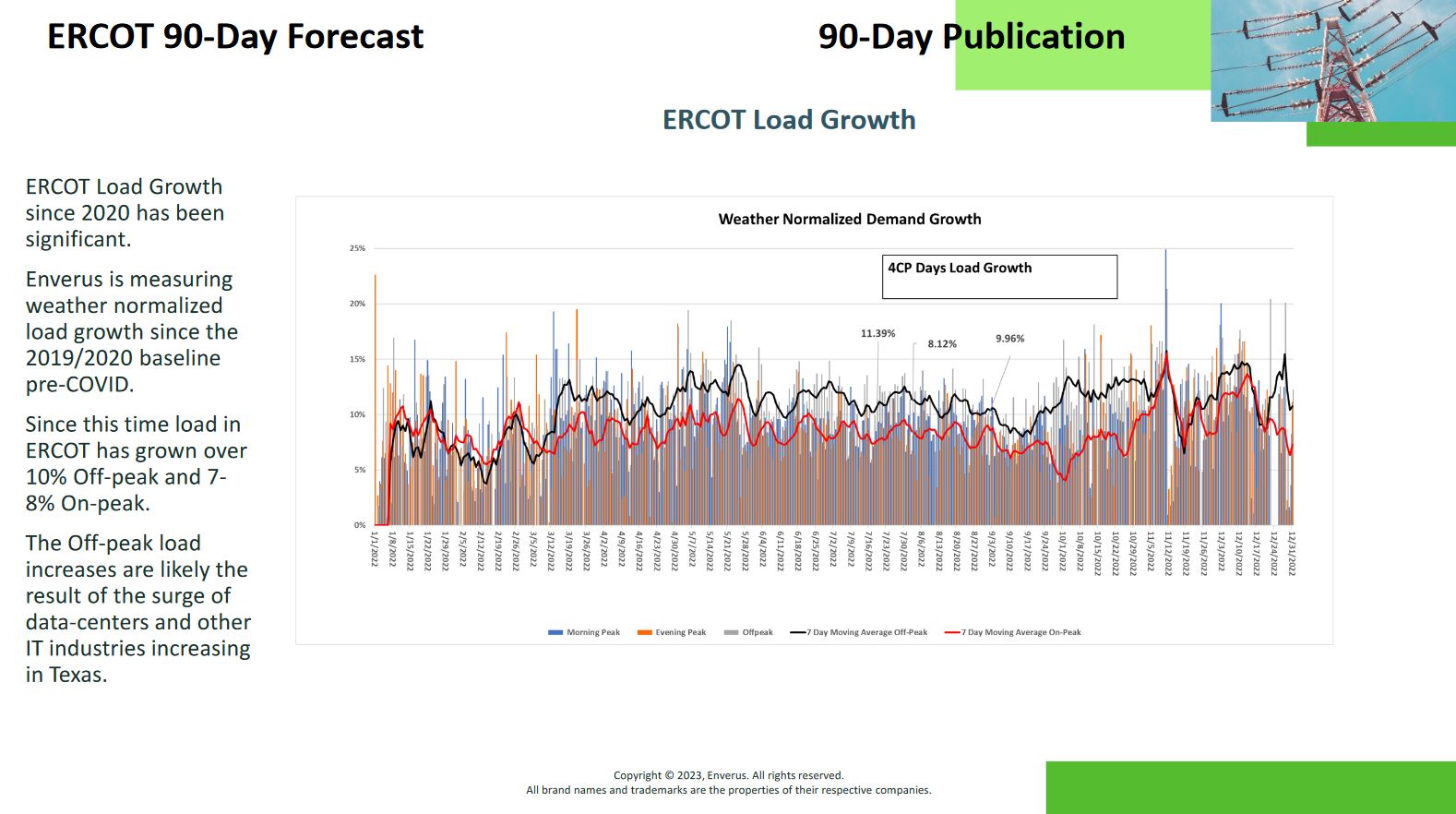
Demand refers to the amount of electricity that consumers need from the power grid at any given time. Understanding an area’s demand is important because it sets expectations for power prices and identifies potential areas where the power infrastructure may not be able to support the demand.
To predict where these potential areas may occur, it is helpful to investigate the expected growth in future load demand in an area, particularly if there are significant increases in demand. Rapid population or industrial growth, as well as the introduction of Bitcoin and rig operators, can result in significant increases in load demand.
It is also important to consider when these demand spikes will occur. For example, Bitcoin miners and some manufacturers require electricity 24/7, which can affect off-peak hours more than morning or evening peaks. Power operators must adjust their operations to meet these changing demands.
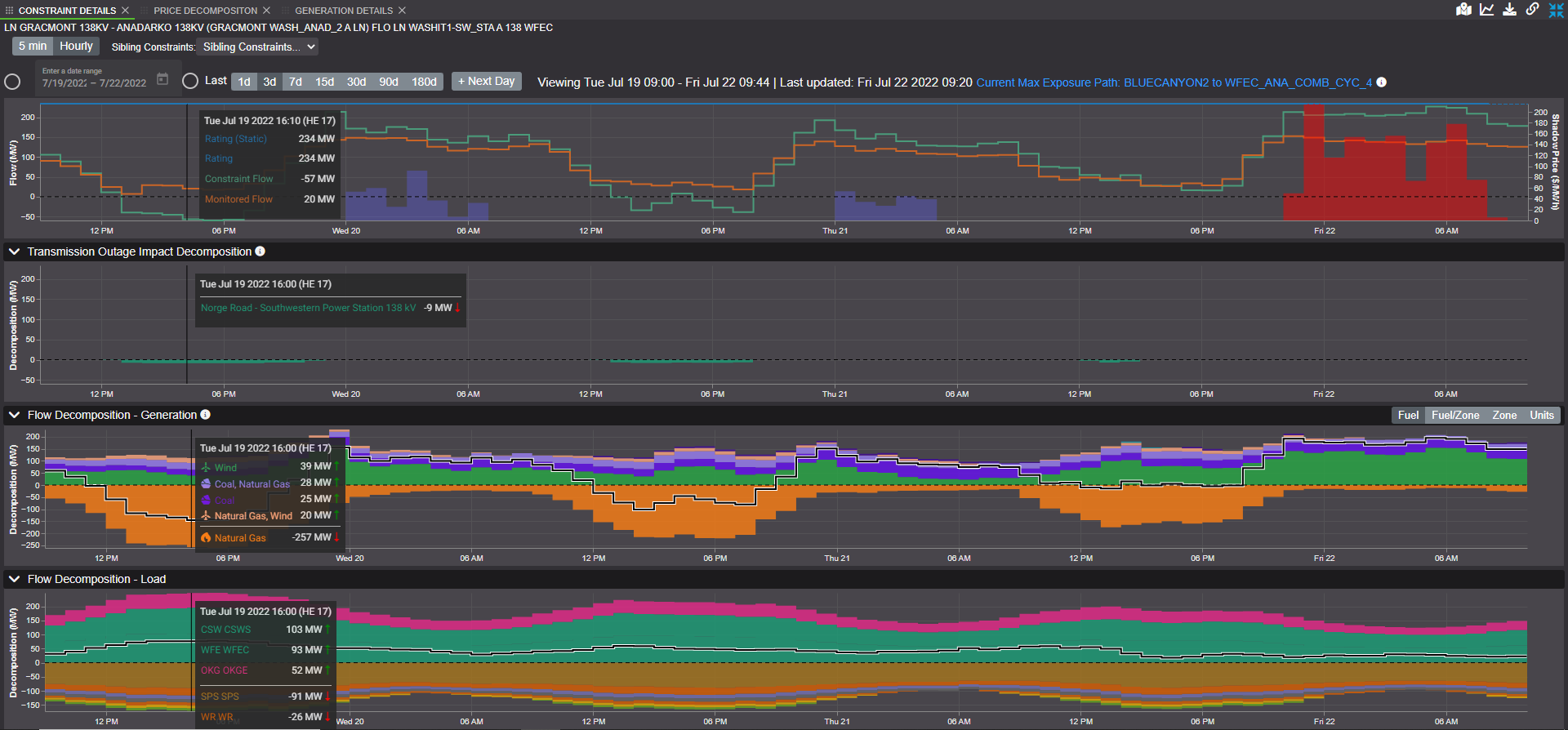
Analyzing past or recent constraints can provide valuable insights and guide future efforts to identify paths that may become constrained. To determine potential paths of interest, it is important to understand the underlying drivers of these constraints and predict whether they will persist in the future. Commercial diagnostic tools are available to aid in identifying the causes of constraints and building a case for their potential continuation.
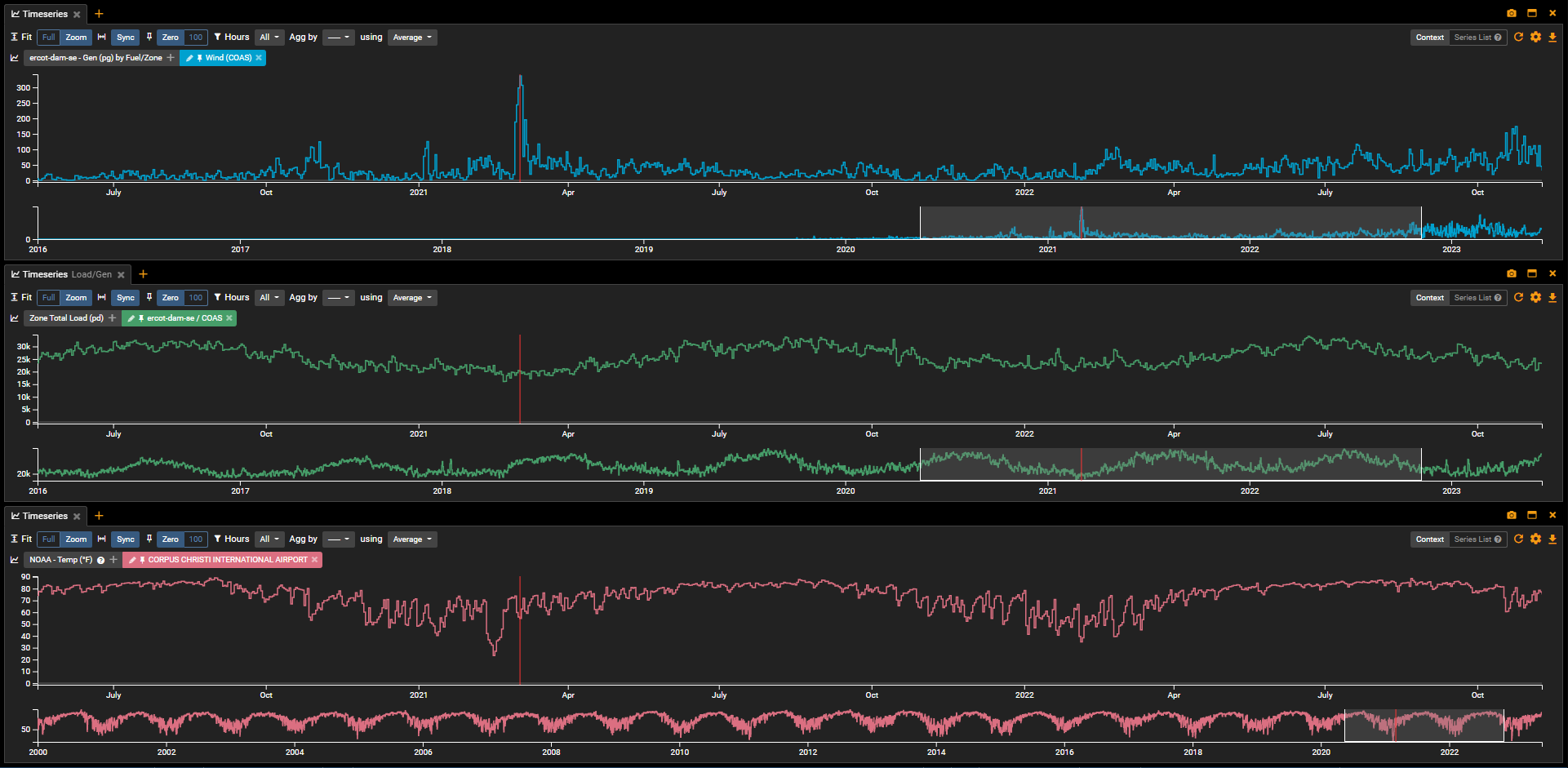
After identifying a constraint driver, it is possible to use constraint analysis tools to simulate different scenarios and assess their impact on the affected paths. For instance, weather scenarios such as high or low wind, cold or hot temperatures can be inputted into the analysis tool to model the grid and identify potential paths that may become constrained. However, running these types of scenarios can be time consuming, and it is advisable to use automated constraint analysis tools to accelerate the process. These tools can significantly reduce analysis time, allowing users to examine hundreds of constraints in just a few minutes and focus on the most interesting paths.
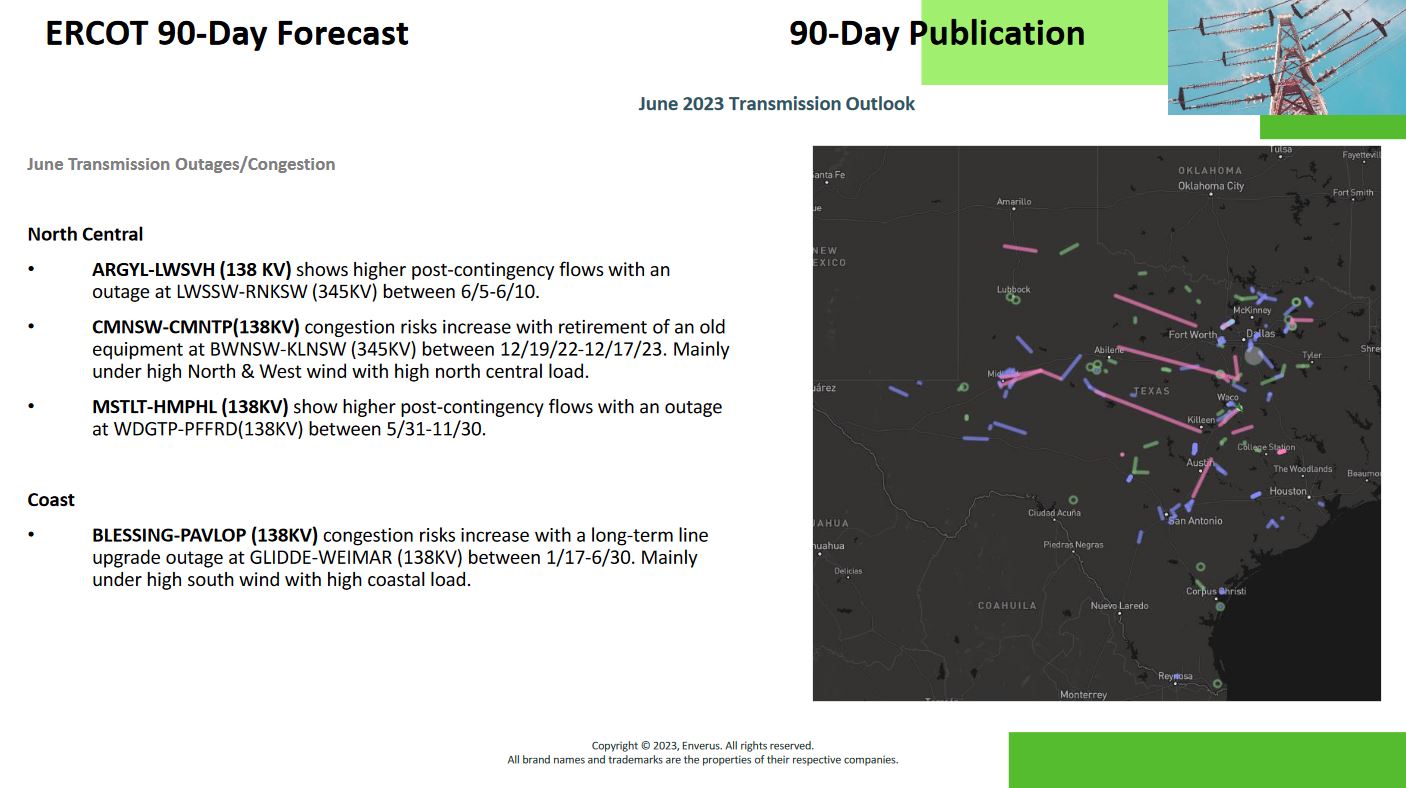
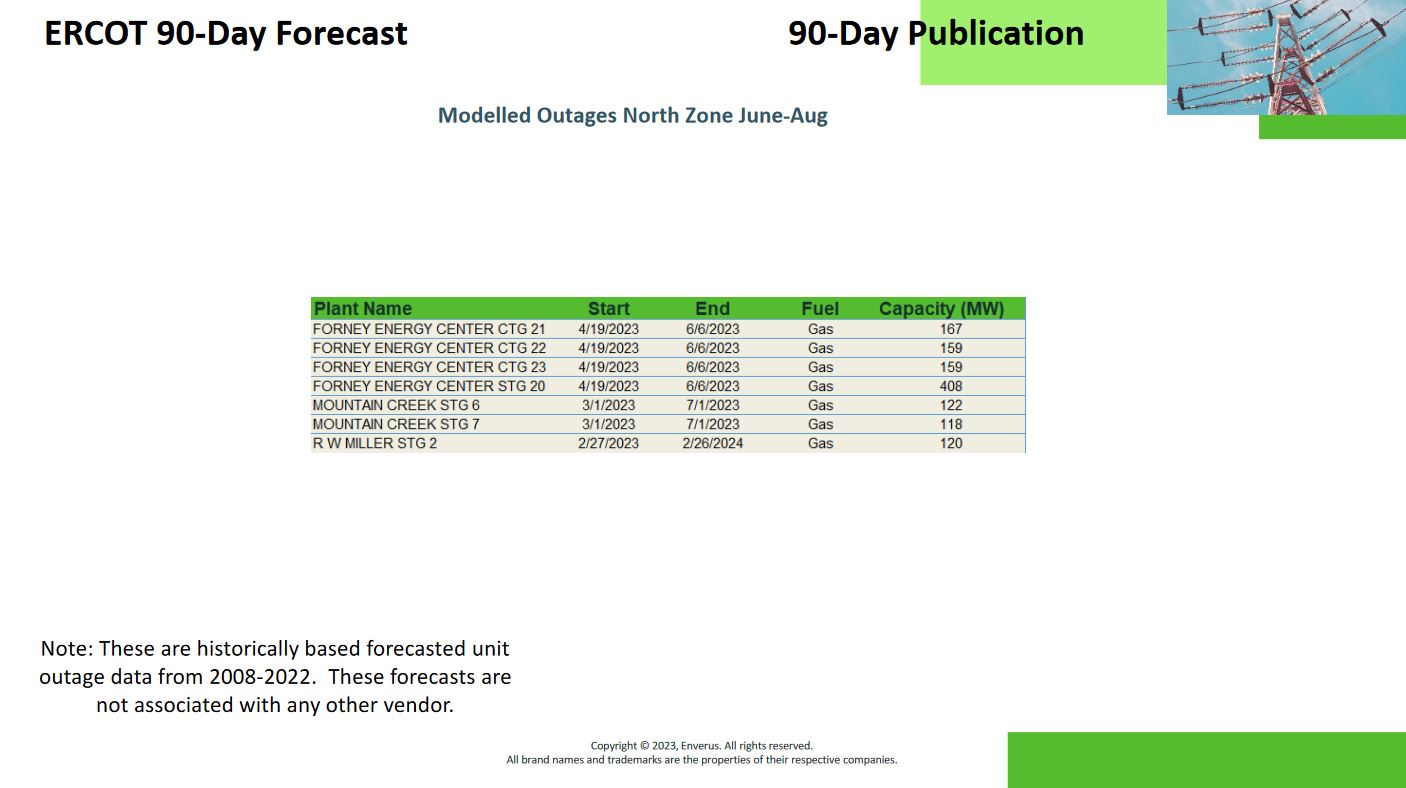
Reports on transmission and generation outages provide valuable information on upcoming maintenance that will impact generation and paths on the grid. Reviewing and understanding these reports can help identify paths with a high likelihood of becoming constrained.
Users can dig into these reports and check historically how these same outages have impacted the grid and which paths had bound. Tools are readily available on the market that simulate the effects of transmission or generator outages on the grid, helping uncover potential paths that bind.
These simulations can be tedious, so it is recommended to use automated tools that can help reduce analysis time, sometimes by tenfold, so that the focus can be on preparing trades instead of analysis.
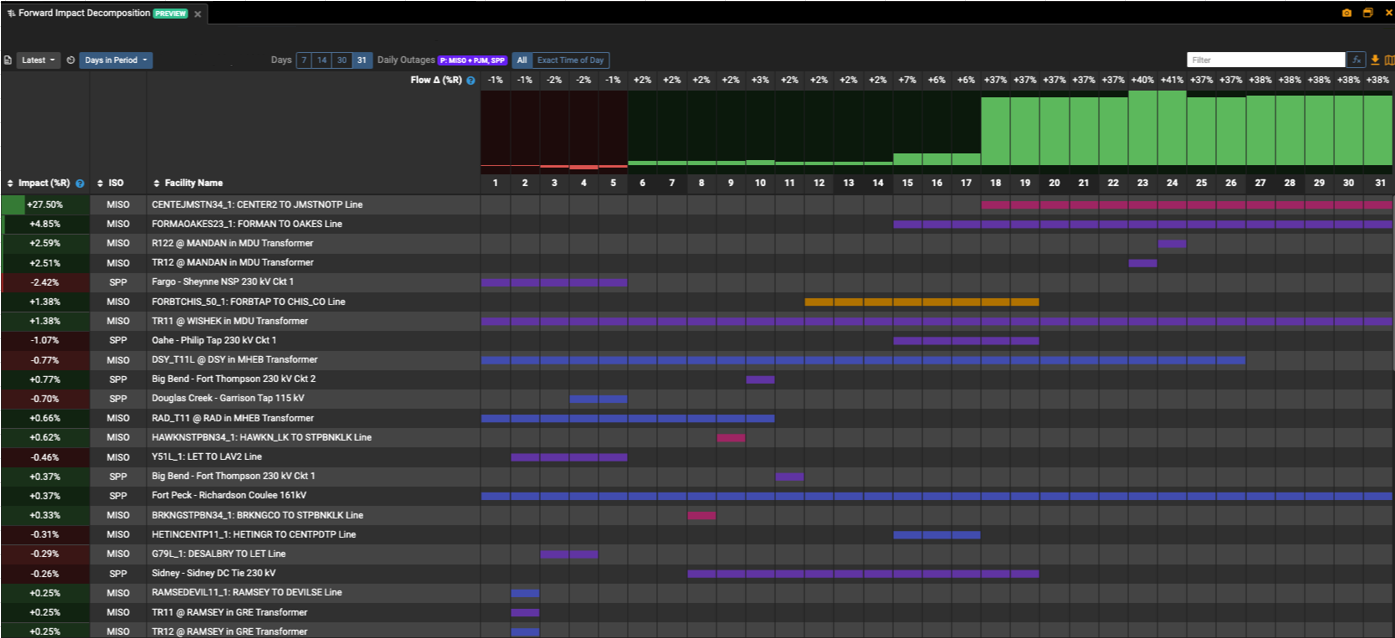
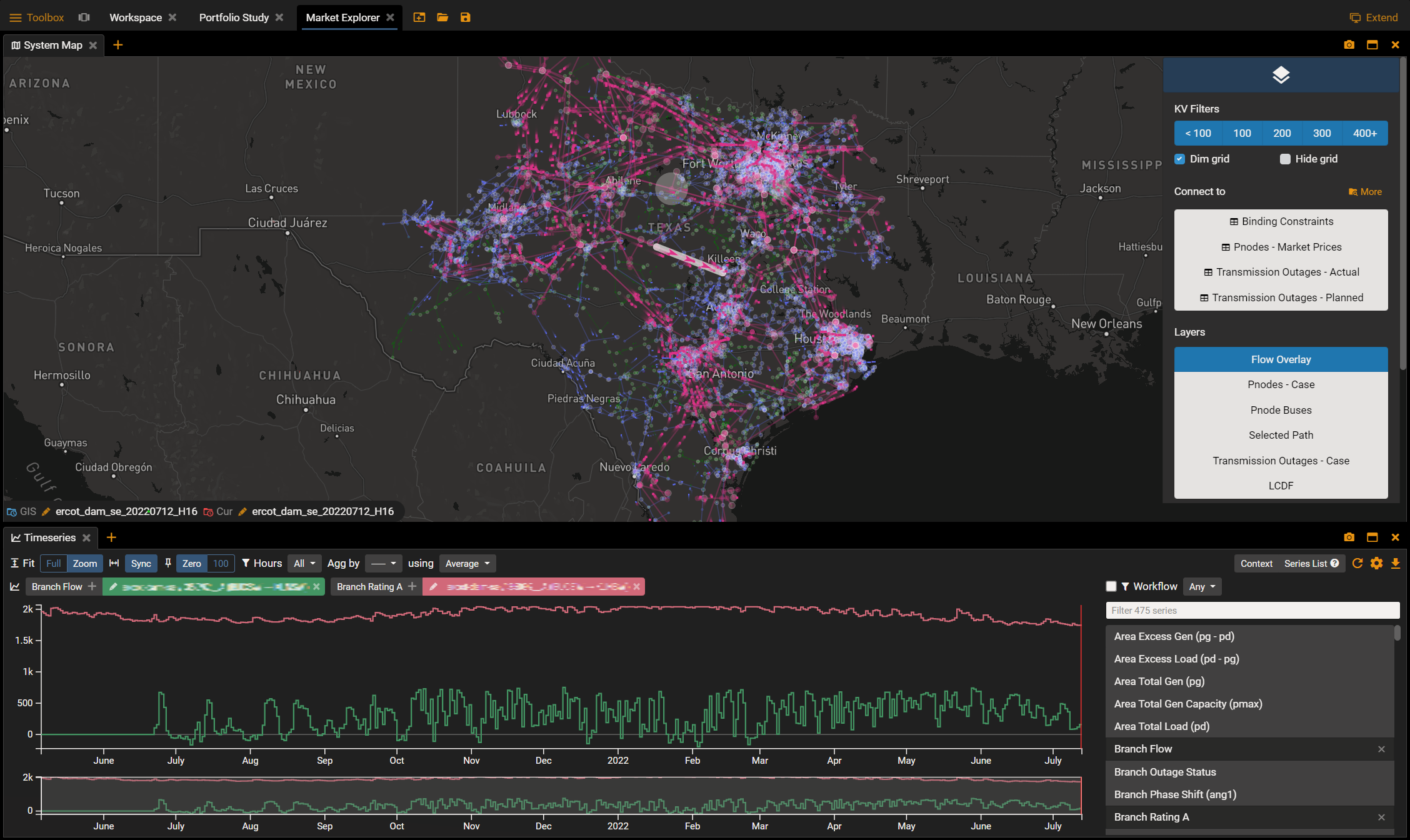
Getting a sense of where and when new generators or transmission lines will come online will bring clarity to what the electricity supply of the grid will look like. Once a date is determined for a new generator or transmission line, users can use tools to analyze its impact on the grid to existing constraints or its potential to create new constraints, bringing new opportunities to look at.
Similarly, when a generator or transmission line is taken offline, analysis can be done to see how its decommissioning will impact the grid.
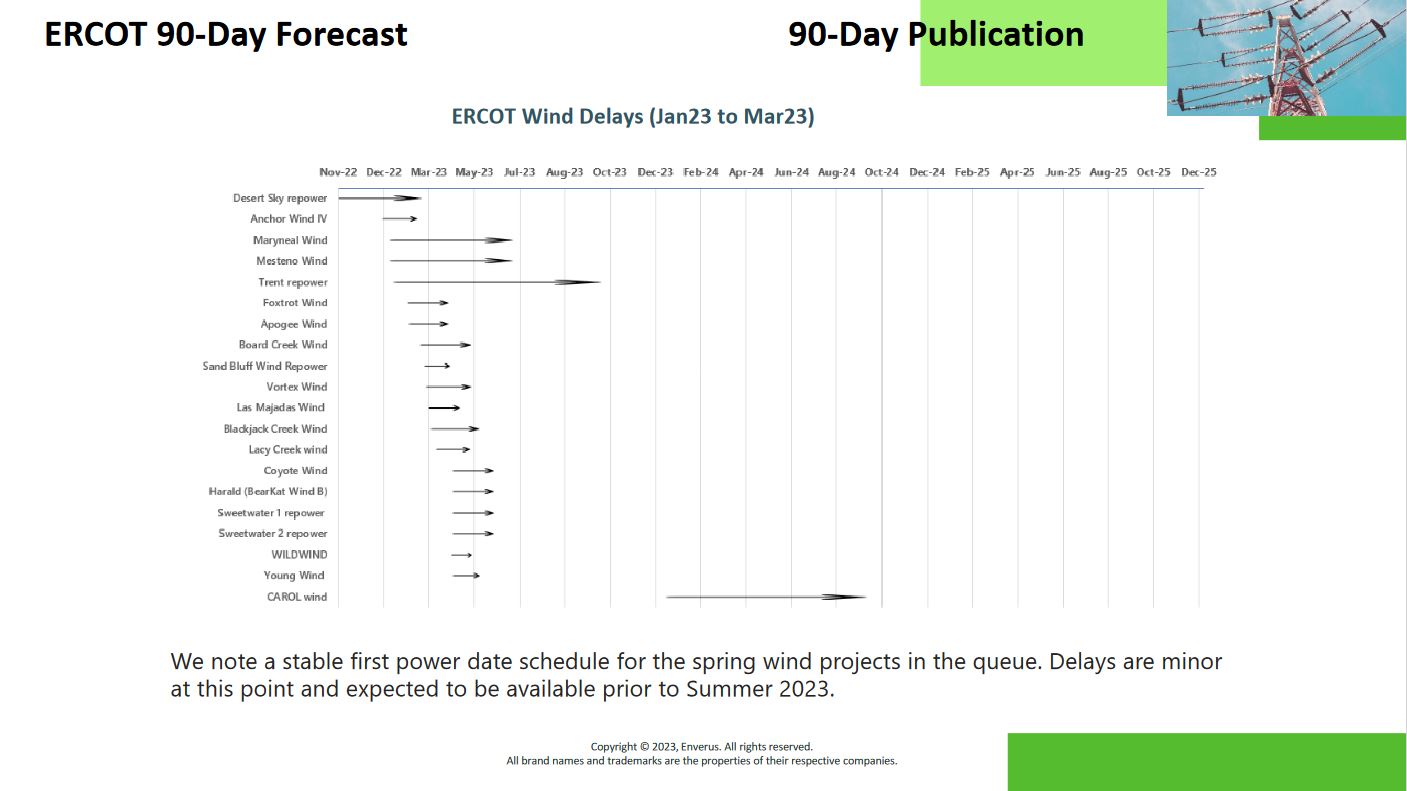
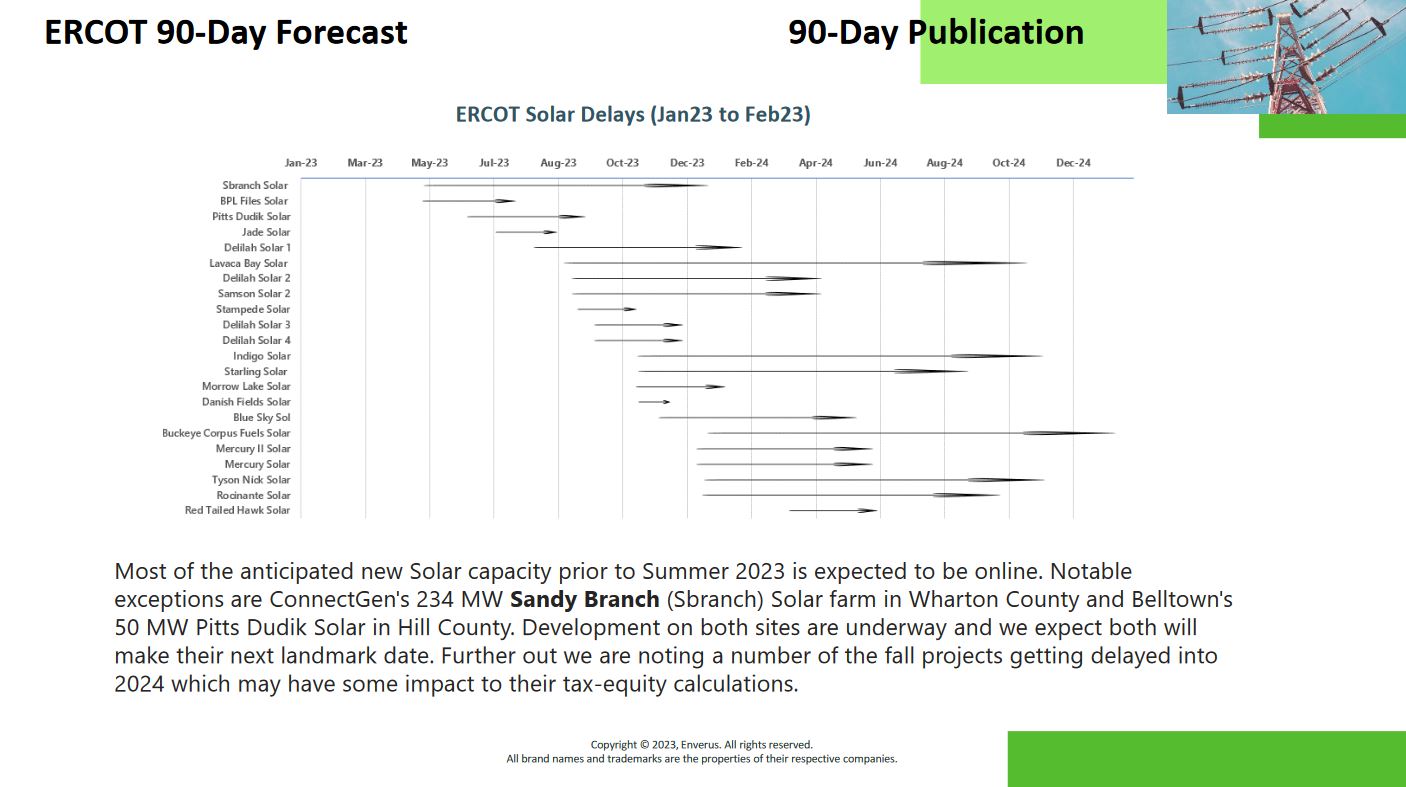
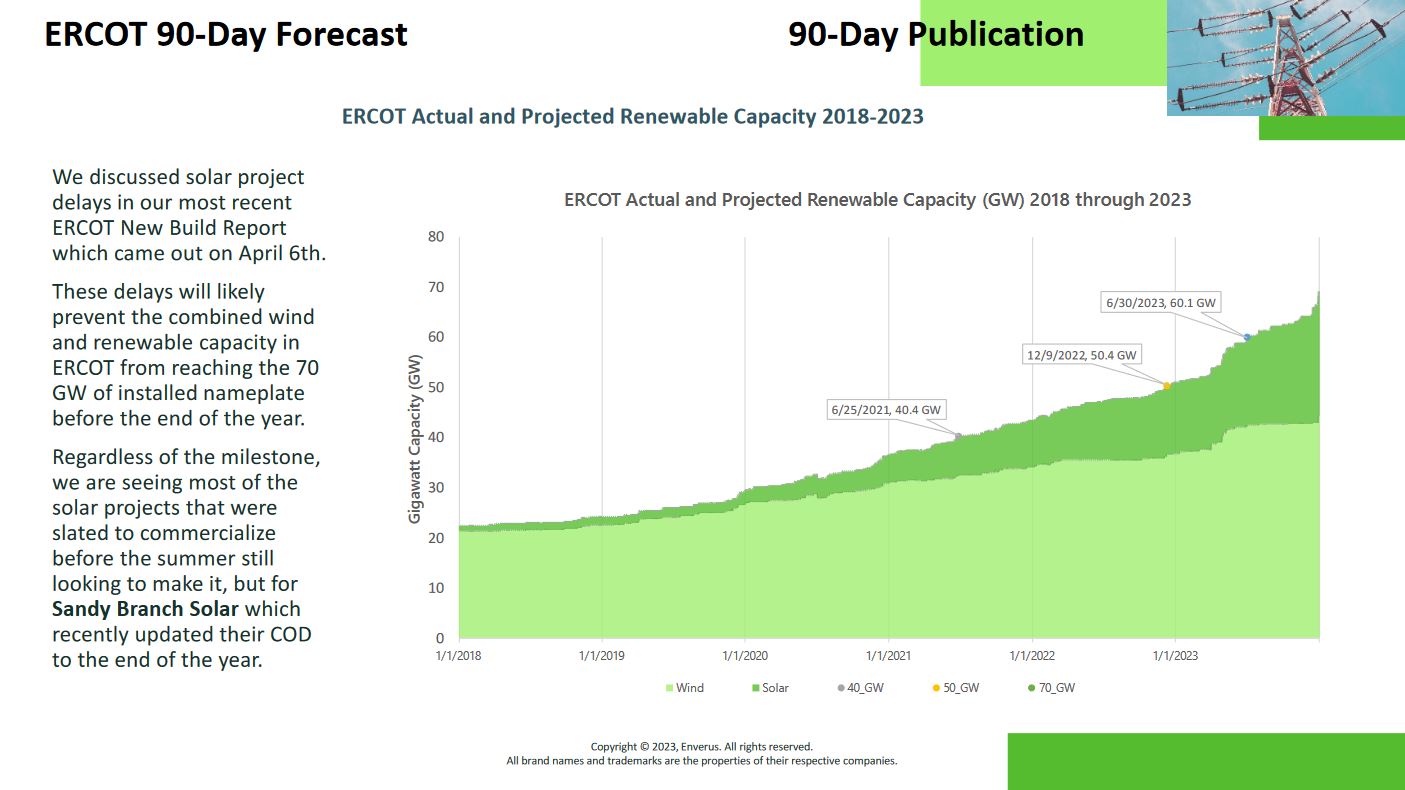
When power projects are delayed, power that was expected to come online will be later than originally anticipated. As a result, positions that were based on those original timelines will need to be adjusted. Staying informed about the latest updates on power project timelines can provide an opportunity for traders to adjust and capitalize on the new projected start date.
When assessing power markets, understanding the future impact of generation and load projects is essential for de-risking FTR trades. Delays in power projects, shifts in projected capacities and new load being built can have an impact on congestion, which will impact trading. For traders to stay informed and agile on these changes on the grid require specialized solutions.
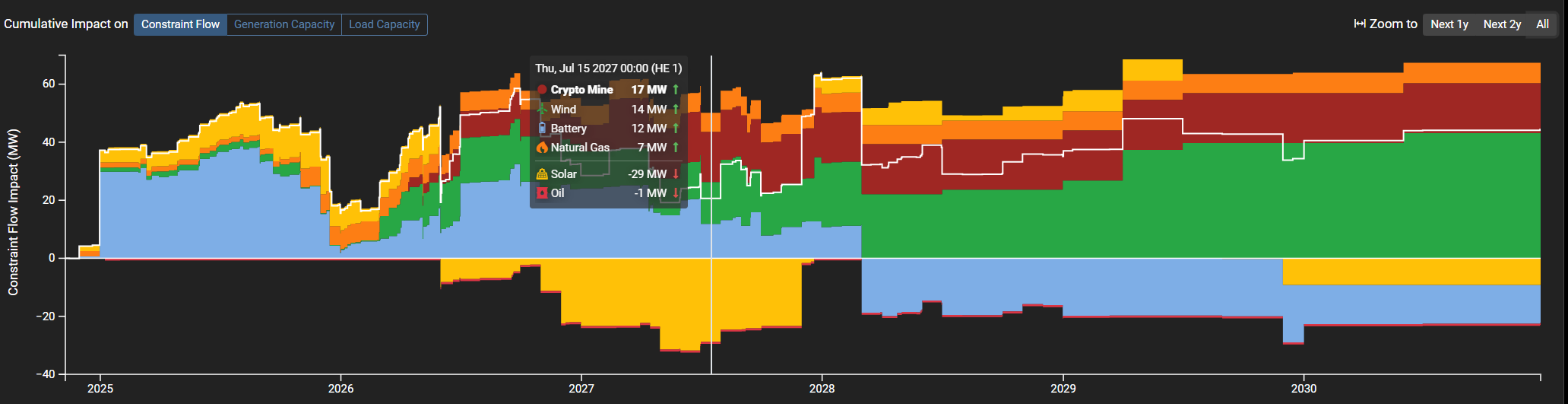
To support this, Panorama integrates tools like Available Transfer Capability (ATC) insights and the new Available Withdrawal Capability (AWC) feature, providing traders with a clearer picture of both generation and load impacts on grid congestion. AWC informs users how much load the grid infrastructure can currently support—and how much it is projected to support in the future. This feature is particularly valuable as load-intensive facilities, such as data centers, crypto mining operations or large industrial centers, increasingly come online. These large loads can significantly impact congestion when added to the grid, intensifying the need for FTR traders to closely monitor AWC metrics alongside generation data.
In addition, Panorama’s Projected Capacity Impact feature enables traders to see how planned generation projects might influence grid constraints. This data, combined with insights from Enverus PRISM® on project tracking, allows traders to proactively adjust positions based on both real-time updates and forecasts of future grid conditions. With the added dimension of AWC, traders gain an enhanced ability to anticipate and respond to the dual pressures of generation and load on grid congestion.

It is important to keep on top of regulatory changes as they can have a significant impact on the power markets. For example, changes in regulation could affect the cost of generation, transmission or distribution of power, which will impact your trading strategy. Additionally, regulatory changes could lead to changes in the availability of FTRs or the rules governing their trading, which could also affect the market dynamics and FTR prices. Reports and analysts are available in the market who regularly stay on top of these changes and summarize and report on the changes to help make sure FTR traders are up to date on the regulation and its potential impact for FTR auctions.
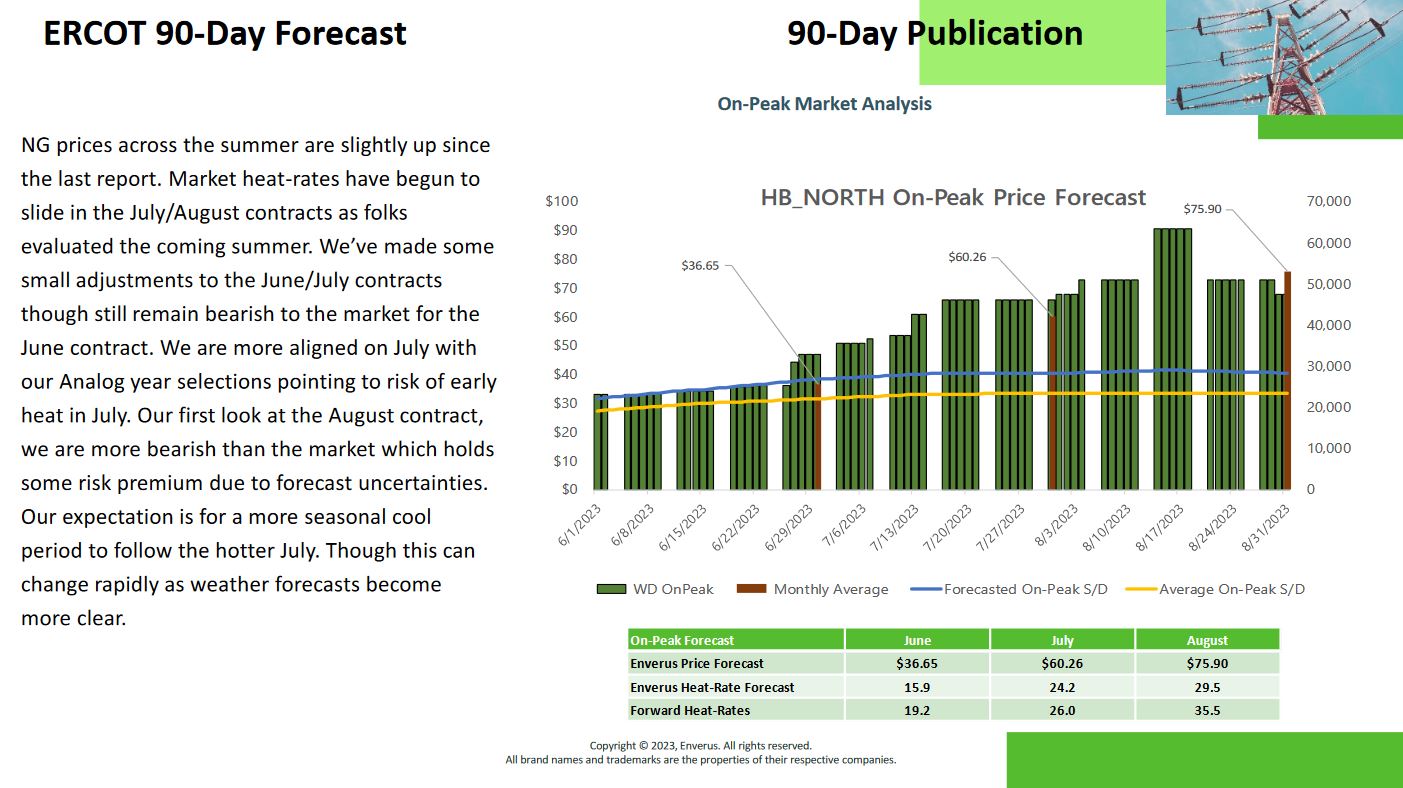
After completing the analysis and identifying attractive trading constraints, it is essential to determine the appropriate price to pay for them. Fortunately, there are numerous tools available that can forecast prices and break down the drivers of congestion costs, allowing users to understand where the congestion price is coming from. Additionally, traders can use tools to view other traders’ portfolios and trading activities, providing insights into which paths are worth pursuing and at what price. For a more in-depth discussion of pricing tools and strategies, a separate e-book will be available.
Discover
About Enverus
Resources
Follow Us
© Copyright 2024 All data and information are provided “as is”.